Logistics
A Key to Vendor Compliance: How to Develop or Integrate EDI Software for Logistics
Some technologies stand the test of time. Electronic data interchange technology (aka EDI software) in the logistics industry is one of them: a standard meant to automate manual information exchanges.
In an age where time is money, EDI is incredibly fast. Its ability to process information at lightning speed not only boosts operational efficiency but also leaves no room for human error or security vulnerabilities. Instead of dealing with situations where retailers have to remind suppliers about invoices through email and drown in paperwork, businesses opt for automated EDI software enabling effortless electronic communication.
In this article, we explore the role of EDI technology, its functioning, and impact on vendor compliance. We also discuss compatible systems, and point out potential challenges during the implementation process to give you the insights you need to make the most of it.
What is EDI software in logistics?
You can think of EDI software as the ultimate communication tool and the backbone of efficient data exchange in logistics. It serves as a common language and platform for businesses, enabling them to transmit various types of critical documents and information electronically rather than relying on paper-based or manual processes.
EDI software operates by translating data from its original format into a standardized format that all parties in the supply chain can process. It typically includes functionalities for data validation, encryption, and secure transmission. EDI logistics software is used for various purposes, such as exchanging purchase orders, invoices, shipment status updates, bills of lading, and other supply chain-related documents with suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders.
The primary factors driving EDI demand, as indicated in the Deloitte survey, are addressing the need for reliability.
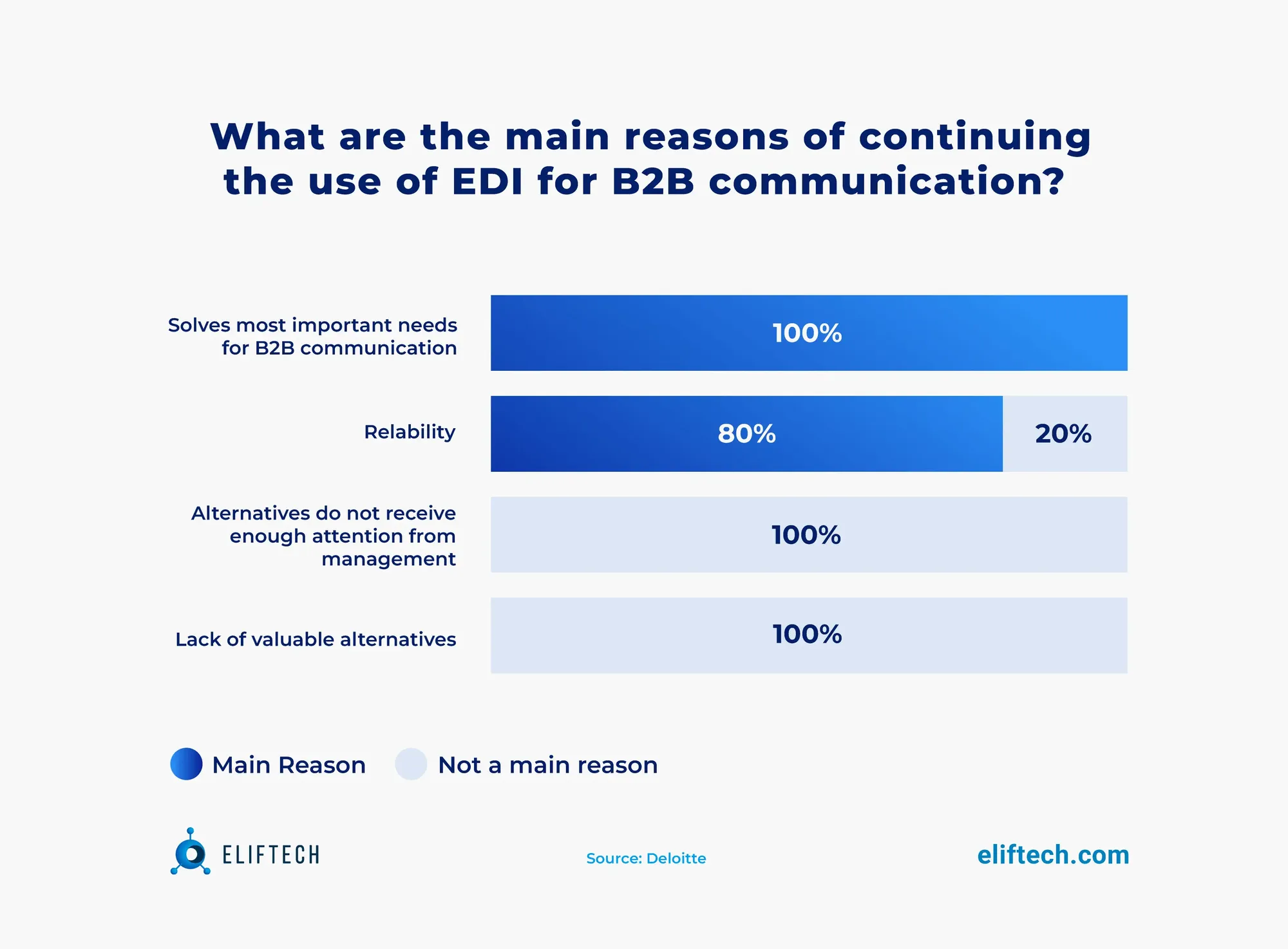
Why EDI compliance in logistics matters
EDI compliance is important due to multiple factors, but the most important ones are as follows:
- EDI compliance guarantees standardized communication across the logistics spectrum. When everyone follows the same rules, there's minimal room for confusion, reducing the chances of costly errors and misinterpretations.
- EDI compliance helps follow logistics regulations. Otherwise, non-compliance can lead to fines, penalties, and operational disruptions, which no business can afford.
- Clarity and trackability. It's like having a GPS for your logistics, allowing you to track shipments, monitor inventory levels, and respond swiftly to market fluctuations.
- Reducing the risks of the human factor. By automating procedures, businesses no longer need to enter data manually, thereby lowering the possibility of mistakes. Companies may operate at lower costs and allocate resources more effectively.
How EDI software works
EDI-compliant software acts as a mediator, translating, transmitting, and integrating data between businesses.
Here's a simplified breakdown of how EDI software works:
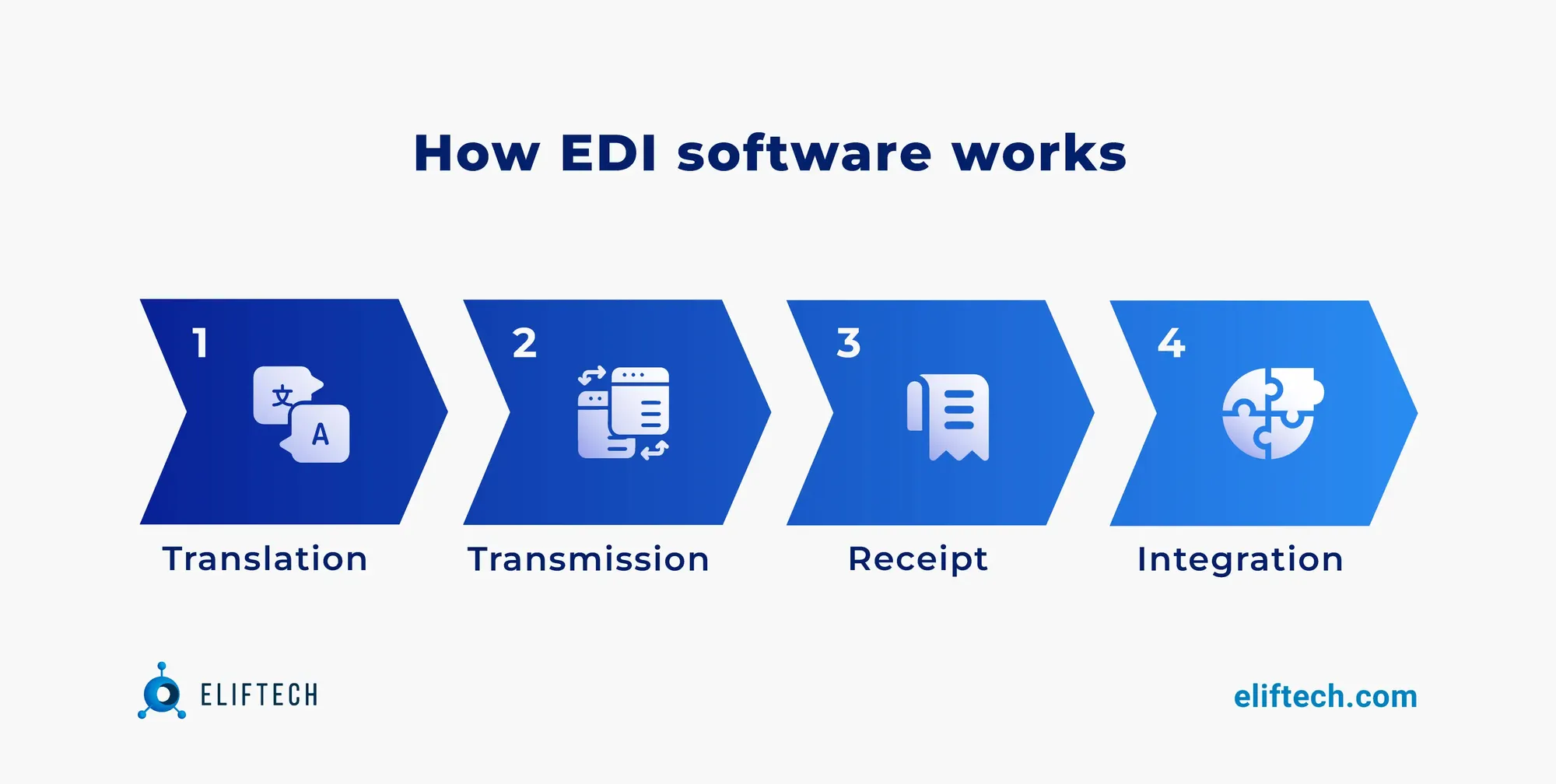
Step 1. Data Translation. When a business initiates an EDI transaction (e.g., sending a purchase order), the web-based EDI software translates the data from the company's internal format (such as XML or CSV) into a standardized EDI format, which follows specific industry or global standards like ANSI X12 or EDIFACT (the most used standard by European retailers). This translation ensures that both the sender and receiver can understand and process the information.
Step 2. Data transmission. Once the data is converted into the EDI format, the EDI logistics software securely transmits it to the recipient using various communication methods like FTPS, PEPPOL, AS2, and VAN (the most frequently used standards in the retail sector). Depending on the particular business requirements, this communication can take place in real-time or in accordance with a predetermined schedule.
Step 3. Data receipt. On the recipient's end, their EDI software receives the incoming data. It then reverses the translation process, converting the standardized EDI format back into a format compatible with their internal systems.
Step 4. Data integration. After translation, the acquired data is immediately imported into the business applications of the recipient, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or EDI ERP software, warehouse management software EDI, or inventory management systems. This integration ensures that the data is seamlessly integrated into the operating procedures of the recipient.
Moreover, throughout this workflow, if any issues or errors occur during the EDI process, such as missing or incorrect data, EDI management software typically provides error-handling mechanisms to identify, report, and rectify these problems. This helps businesses maintain data quality and resolve errors promptly.
What EDI Does for Logistics Operations
EDI software systems reduce manual paperwork for everyone involved in the transportation journey.
For example, exporters need to prepare piles of documents, including invoices, certificates of origin, and export declarations, after processing a purchase order. EDI streamlines the exchange of export documentation. It accelerates customs clearance and minimizes the risk of delays or errors in documentation, ensuring on-time shipments.
Freight forwarders and NVOCCs (Non-Vessel Operating Common Carriers) also tend to wait for agents, who can spend many additional hours creating a bill of lading and identifying the suitable carrier for a specific situation. With an EDI system, they can easily communicate with freight forwarders or NVOCCs to transmit the documents as soon as they are prepared.
Web-based EDI software solutions connect freight carriers with exporters and custom agents. After setting the freight rate, the documents go to the company moving the goods, whether it's a trucking or ocean carrier. Using EDI trucking software, they easily check the standardized documents. The EDI system then updates the exporter in real-time about the shipment's status, improving communication between them and the carrier.
An EDI system also makes custom brokers' lives simpler, allowing exporters to send them their export documents. If there are issues with a shipment, the EDI system provides exporters with updates on the reasons for customs delays.
Technologies Shaping EDI Systems in Logistics
Advancements in technology are continually shaping EDI systems in logistics. From cloud to EDI software integrations with TMS and ERPs to accounting software and APIs, these innovations continually enhance its capabilities.
Cloud technology. The migration to cloud-based EDI solutions offers businesses scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, allowing them to deal with thousands of EDI transactions. Moreover, it costs less than running a traditional on-premise solution.
System integrations with TMS, ERP, WMS, SCM, and accounting software. EDI integration software with other essential logistics business systems enhances comprehensive supply chain visibility and automates crucial processes through a single, consolidated tool. For instance,
- EDI + TMS provides real-time insights into transportation processes, enabling efficient route planning and load optimization. EDI freight forwarding software brings automation to freight tendering, shipment tracking, and carrier communication for faster delivery times and cost savings.
- EDI + ERP or EDI inventory software or EDI ERP software makes data and business intelligence work hand in hand. This combination enhances inventory management, supports informed decision-making, and optimizes order-to-cash and procure-to-pay cycles. As a result, errors go down, and efficiency goes up.
- EDI + WMS or warehouse management software EDI offers real-time visibility into inventory levels, order statuses, and warehouse operations. This, in turn, ensures precise order fulfillment, reduces stockouts, and enhances overall warehouse efficiency through streamlined processes.
- EDI + SCM enhances end-to-end supply chain visibility. This includes demand forecasting, supplier management, production planning, and distribution optimization. The result is a more agile and responsive supply chain capable of adapting swiftly to market fluctuations.
- EDI + accounting software or EDI billing software automates financial transactions, from invoicing to payment processing. This leads to more accurate financial record-keeping, reduces manual data entry, and mitigates the risk of errors. Additionally, it simplifies auditing and compliance processes.
Blockchain. Although blockchain technology is still in its infancy in logistics, it offers the potential for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof data exchange. Thanks to its decentralized and immutable nature, it can add an additional layer of trust and traceability to EDI transactions. Major retailers don't put blockchain implementation into their immediate agenda; however, this technology is an excellent solution when it comes to data integrity issues.
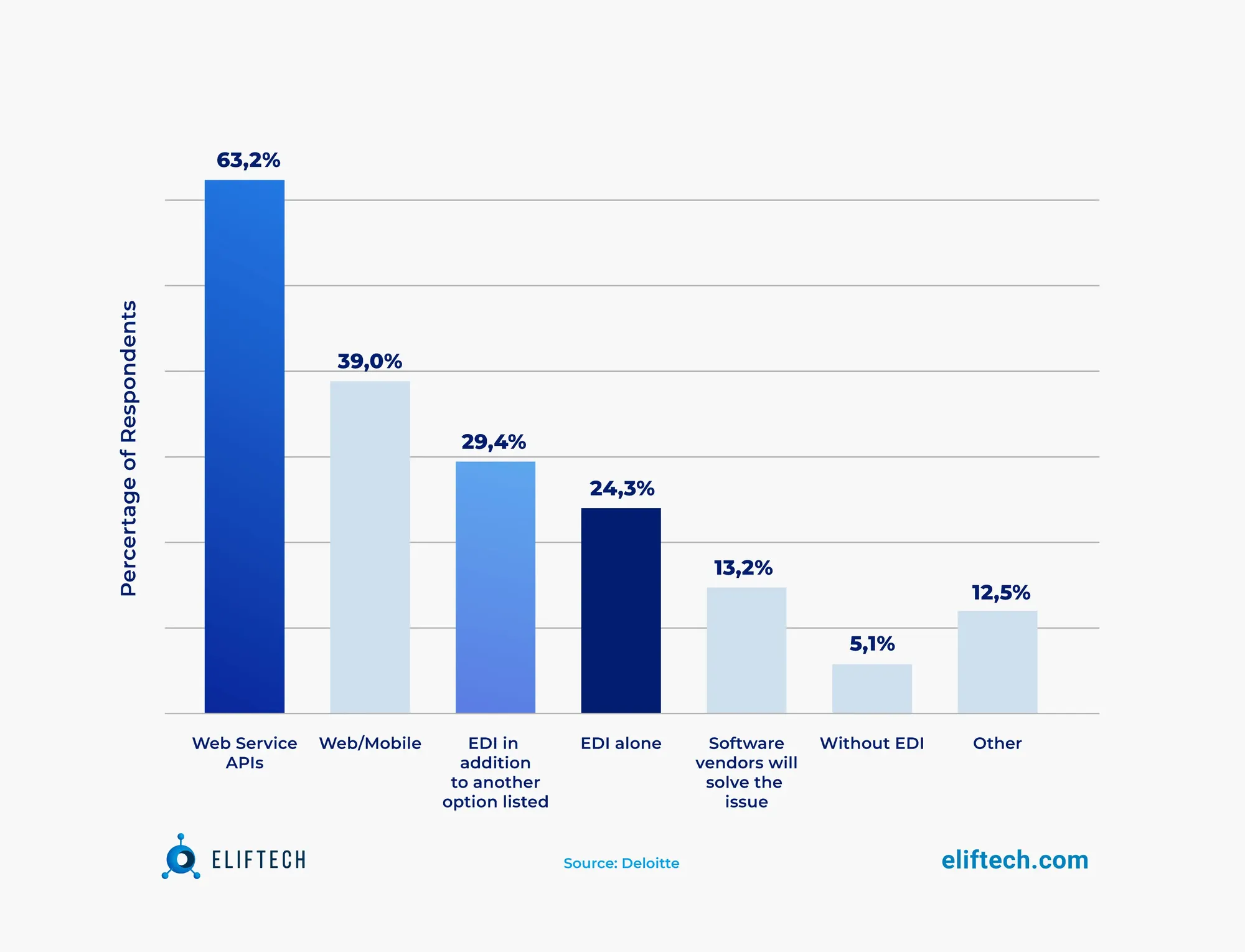
EDI with API integrations
The combination of EDI with APIs seamlessly accommodates various document types, including X12, EDIFACT, XML, and many more, facilitating electronic communication with different partners, customers, and suppliers.
Moreover, a Deloitte survey on the future of B2B communications highlights the substantial increase in the usage of APIs and predicts that other B2B formats will complement EDI.
Ready to streamline your logistics with EDI? Learn how our technology-based logistics solutions can enhance vendor compliance and deftly resolve operational challenges.
Developing Custom EDI Software
Embarking on the EDI software implementation journey, it's essential to leave no stone unturned, meticulously considering all technical and business aspects right from the start.
Step 1. Analyze your business requirements and objectives
It's essential to pinpoint the specific challenges you want to address with custom EDI software solutions, considering the network you work with, each using different documents, standards, and protocols.
This process typically involves identifying specific needs like transaction volume, data formats, system integration, scalability, and security.
Step 2. Choose the right EDI standards and communication protocols
Start by researching the common EDI standards within your industry. For instance, in the United States, the X12 standard is widely used, while EDIFACT is common in international trade. To learn about the prevailing standards and expectations, speak with colleagues and industry organizations.
When it comes to communication protocols, there are several options to consider:
- AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) - a widely adopted protocol for secure data exchange over the internet.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - allows for the simple transfer of files between systems, though it may lack the security features of AS2.
- FTPS (Secure File Transfer Protocol) - combines the simplicity of FTP with enhanced security, making it suitable for sensitive data.
- PEPPOL - provides secure communication over the web and is commonly used for EDI transactions mandatory in some European countries.
- Direct Connection (VAN, VPN) - establishing a direct connection with your partners via a Value-Added Network (VAN) or Virtual Private Network (VPN) can offer a high level of security and control.
Step 3. Take into account key functions EDI software should support
Carefully outline the functional requirements your custom EDI software solutions should support to solve your main challenges. These may include:
- Document generation. Determine what types of documents your business regularly generates: purchase orders, invoices, shipping manifests, etc. Ensure that your EDI management software can seamlessly create these documents in the required formats.
- Real-time document monitoring. This functionality enables you to track document progress, assuring timely deliveries and spotting any transmission problems that might occur.
- Data validation. Your software should include robust data validation mechanisms to ensure that the information exchanged is error-free: data completeness, conformity to standards, and compliance with predefined rules.
- Document reporting. Having reporting capabilities is crucial when interpreting your EDI processes. You should be able to generate performance metrics, assess transaction volumes, locate bottlenecks, track document mistakes, and use reporting capabilities in your software.
- Analytics tools: these can offer insightful data on customer behavior, supplier performance, and transaction patterns to inform strategic decisions and process improvements.
Step 4. Consider choosing a reliable EDI software development partner
When it comes to the EDI software implementation phase, you might lack the technical expertise or capacity to launch the development phase. In such cases, the best solution is to move on your project with an experienced EDI software vendor with a proven track record in providing custom EDI solutions.
If you choose to get it developed this way, your EDI solution will be fully customized to your corporate needs and system integrations. This not only saves you valuable time and effort but also minimizes costs compared to trying to tackle these tasks on your own.
Step 5. Customize and configure the solution
Customize and configure the EDI solution to match your unique business workflows and ensure a smooth transition. It involves aligning data across different systems to meet EDI requirements, establish document storage, and ensure accurate data mapping.
So, pay special attention to data mapping. If not done right, your documents might end up in the wrong places or get lost in your EDI system. Alongside mapping, define clear formatting rules for all your incoming and outgoing documents to maintain accuracy.
Step 6. Run tests and checks
Before fully deploying the software, simulate real-world scenarios to validate the EDI software's quality and identify any weaknesses or inconsistencies. During the testing phase of your EDI system, it's crucial to establish direct communication channels with your carriers, forwarders, and other partners. This ensures that submitted documents are accurately translated and conform to the appropriate EDI formats.
Step 7. Train your team
An educated team is your most valuable asset. Otherwise, there is no point in expecting a rapid, successful response from such a technological adoption. Ensure your team has thorough training and direction to use the software efficiently, deal with exceptions, resolve problems, and adhere to best practices for EDI operations.
Step 8. Keep monitoring and improving your EDI software
The development of custom EDI software should not be considered a one-time process. It is crucial to set up monitoring mechanisms to keep a constant watch on system performance, data flows, and adherence to your objectives. This ongoing improvement process ensures that your EDI logistics software continues to deliver value as your business evolves.
The Potential Challenges in Adopting EDI Software
While EDI isn't a new technology, it does require knowledge, investments, and time, which can appear complex for companies to manage. Here are some of the most common challenges encountered by businesses we’ve worked with, and how we addressed them:
1. Logistic Operations Complexity
Dealing with complex business logic, multiple data formats, and specific industry requirements can complicate the implementation process. However, these challenges can be effectively addressed before development.
For example, aligning the various players’ EDI processes is crucial. Together with your partners, you may find that customizing the EDI solutions is the right approach. Customization ensures that the system can efficiently handle various document types, work seamlessly with different partners, and meet industry-specific rules and regulations.
2. Financial Considerations
The challenge of financial considerations in EDI adoption has two extremes. On one hand, small businesses may view the initial investment in EDI as a substantial financial burden. On the other hand, large corporations, while having more financial resources, may face the challenge of optimizing ongoing EDI costs efficiently.
Some strategies can help minimize this concern.
Strategy 1. Budget planning
- Small businesses can explore cost-effective EDI solutions that align with their financial capacity and meet their current and future needs.
- Large corporations can consider consolidating EDI software services, negotiating with service providers, and exploring cloud-based solutions that offer scalability without significant upfront costs.
Strategy 2. ROI analysis
A thorough ROI analysis will help understand how EDI implementation can positively impact business operations by highlighting potential cost savings and efficiency improvements in the short and long term.
Strategy 3. Collaboration with reliable service providers
For both small and large businesses, collaboration with EDI service providers is instrumental. These providers offer insights into cost-effective solutions, provide guidance on EDI best practices, and help organizations make informed financial decisions.
3. Resistance to Change and Technical Capacity
A lack of digital maturity, a commitment to traditional methods, and technical shortages are common roadblocks that can hinder a company's path to growth. The problem is obvious from three different perspectives:
- Employees could worry that EDI automation would change the nature of their jobs.
- IT departments may need to reassess their technical capacity to support the implementation and maintenance of EDI systems.
- Business leaders may lack a clear vision for how EDI fits into the company's future.
Businesses can first identify the teams that need support, and then they can provide training programs to fill up the skill gaps. Or, senior management can also start corporate-wide campaigns highlighting the advantages of EDI automation and involve workers in the decision-making process.
Measuring the Impact of EDI on Vendor Compliance
When it comes to measuring the impact of EDI on vendor compliance, we highlight the following KPIs:
Reduced logistics costs and zero paperwork
An EDI system centralizes all paperwork into a single electronic platform, simplifying data exchange between your company and your partners. This reduces the burden of paperwork and lowers operational costs associated with manual processes.
Seamless B2B document exchange through automation
An advanced EDI system automates the exchange of logistics documents among all stakeholders, reducing the risk of errors and delays within the supply chain.
Better receiving procedures
Some EDI software features include electronic packing lists, advanced shipping notices (ASNs), and automated inventory updates. These features inform companies about what to expect from incoming shipments and when they will be delivered. As a result, your staff no longer needs to process them manually and barcode each unit upon receiving goods.
Document consistency
EDI enforces standardized data formats and communication protocols for document exchange. As a result, there is a lower possibility of misunderstanding, disputes, or misinterpretations.
Conclusion
Incorporating EDI-compliant software into logistics is essential for any logistics company looking to secure its future in supply chain management. It continues to be the go-to solution for standardized B2B communication, ensuring efficiency and compliance.
Even if you simply don’t have competent staff, experience, or resources, there are always EDI software development companies that can help bridge these gaps. In case you opt for collaboration with ElifTech, you will:
- Customize EDI software by integrating third-party tools like EDI systems, shopping carts, marketplaces, and financial reporting tools.
- Improve logistics processes through innovative technology, including the cloud, blockchain, ML and AI, big data, and APIs.
- Optimize logistics processes., including improved vendor compliance and broad compatibility with various standards and formats.
- Get ongoing project support for your logistics needs.
Contact us to make EDI a common language across your supply chain processes, unlocking benefits like real-time data exchange, error reduction, faster order processing, improved accuracy, and strengthened vendor relationships.
Browse our case studies and get actionable insights to drive your success
See more