FinTech
FinTech Legacy System Modernization: Key Strategies
Established businesses may recognize the necessity of incorporating digital innovations and enhancing customer experience for success. What they may not realize yet is that achieving this requires a profound transformation in their operations, and this includes giving serious thought to legacy system modernization.
When it comes to modernizing legacy applications, the ideal strategy depends on the specific issue you are addressing. The push for digital transformation has necessitated that application leaders identify efficient methods for updating their legacy systems. The greatest hurdle? Determining the risk-to-reward ratio before taking action.
Legacy systems are often perceived as impeding business initiatives and processes in many organizations. A staggering 79% of bank leaders firmly believe that their bank's survival hinges on this crucial modernization, enabling them to innovate at a faster pace. This drive for digital transformation presents exciting opportunities for collaboration between traditional financial organizations and innovative fintech companies.
In this article, we'll explore the world of legacy systems in the financial industry, and uncover how collaborating with fintech companies can empower financial institutions to enhance their solutions, elevate customer experiences, and pave their way for a successful digital transformation journey.
What is Legacy System Modernization in the Financial Industry?
The financial industry has a long history of utilizing various technological systems and infrastructure to support its operations. However, as technology advances at an unprecedented pace, many financial institutions find themselves grappling with the challenges posed by legacy systems.
A legacy system refers to outdated technology, software, or processes that have been in place for a considerable period of time. These systems have often served financial institutions well in the past, but their limitations become increasingly apparent as the industry evolves in the digital era.
Legacy systems in the financial industry encompass a wide range of components, including enterprise software for legacy modernization, databases, and communication systems. These systems are typically characterized by outdated technology standards, incompatible interfaces, and architectures that do not align with current industry trends.
While legacy systems may have been efficient and effective at the time of their implementation, they now face numerous challenges in meeting the demands of the modern financial landscape. These challenges include compatibility issues, inflexibility and scalability, limited compliance capabilities, and data and process silos.
Recognizing the need for change, the financial industry is increasingly prioritizing legacy system modernization. The benefits of upgrading legacy systems in the financial industry are numerous and can include:
- Improved scalability and adaptability to meet evolving business requirements
- Enhanced efficiency through streamlined processes and the elimination of redundant or manual tasks
- Better compliance capabilities and adherence to industry regulations
- Access to cutting-edge technology
- Seamless integration with other systems, promoting efficient collaboration and facilitating information sharing across different platforms
- Personalized experience for customers
Nonetheless, legacy system modernization cannot be approached with a one-size-fits-all mindset as it necessitates tailored solutions for each financial institution, considering their distinct requirements and challenges. Collaborating with experienced FinTech companies can help navigate this complex journey, ensuring a tailored and effective solution that aligns with the institution's goals and objectives.
Limitations and Drawbacks of Legacy Systems
Legacy systems present several challenges and limitations that hinder the efficiency and effectiveness of financial institutions. First and foremost, these systems are often characterized by outdated technology and infrastructure, which can lead to compatibility issues and hinder seamless integration with new systems. This incompatibility prevents financial institutions from adopting new technologies that can greatly enhance operations and customer experiences.
Furthermore, legacy systems are typically inflexible and lack scalability. They are designed to cater to specific processes and structures, making it difficult to adapt to rapidly changing business needs. On the contrary, the financial industry is currently propelled by dynamic market conditions and continuously evolving customer demands. The inability of legacy systems to accommodate these changes effectively hampers the ability of financial institutions to remain agile and competitive.
Another drawback of legacy systems is their limited compliance capabilities. As regulations and compliance requirements become increasingly stringent, financial institutions must ensure that they can meet these standards. However, legacy systems often lack the necessary features and functionalities required for compliance, leading to potential legal and security risks.
Moreover, legacy systems are plagued by data and process silos, hindering the flow and accessibility of critical information across different departments and systems within an organization. This fragmentation reduces operational efficiency and limits real-time data analysis, which is crucial for making informed business decisions in today's fast-paced financial landscape.
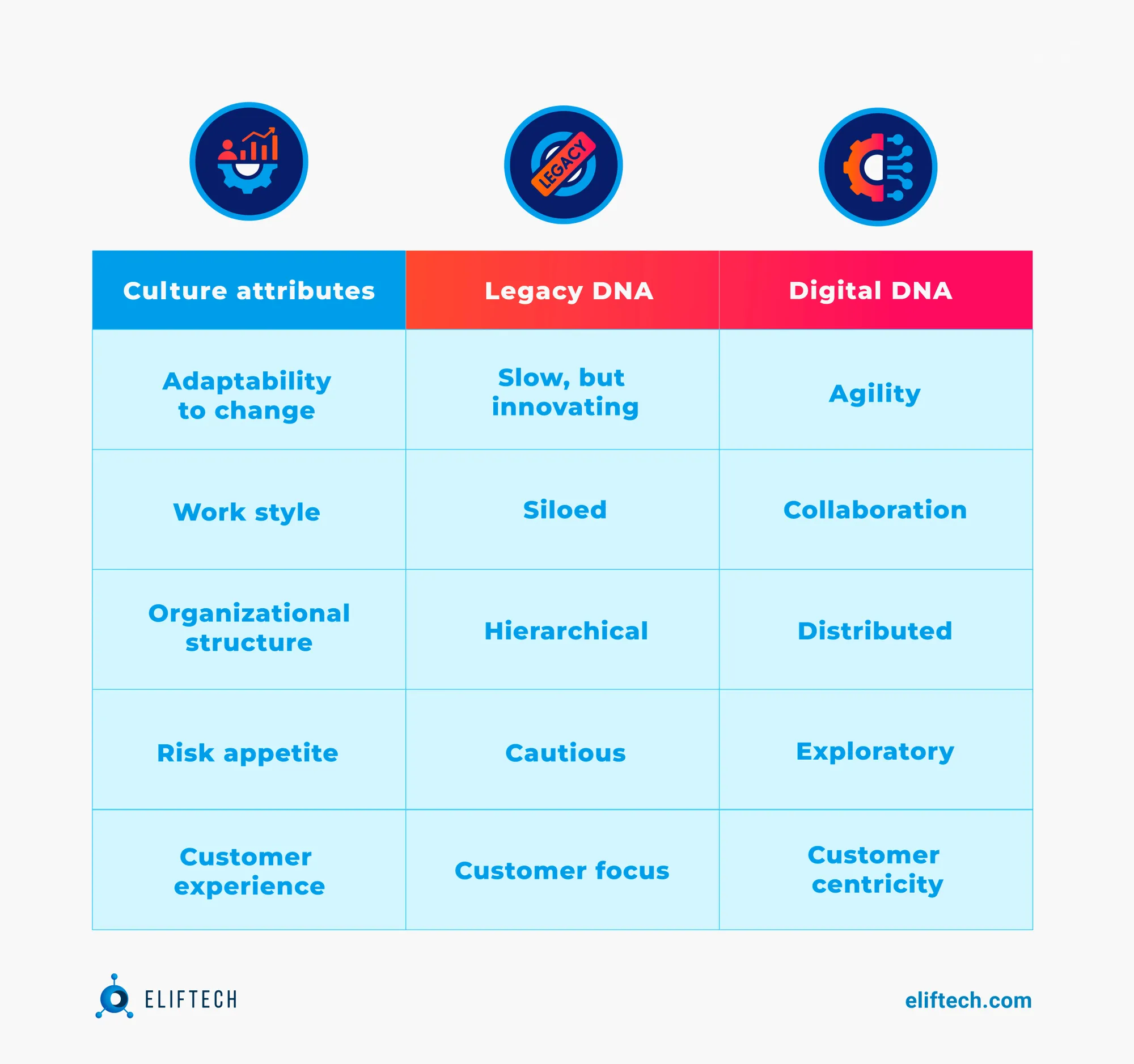
Deloitte's report "Digital Transformation in Financial Services: The Need to Rewire Organizational DNA" highlights that legacy systems continue to be a challenge for organizations in the financial industry. Larger organizations, including government agencies, may continue to use outdated systems due to their extensive operations and complex internal structures. Traditional financial institutions, such as banks and credit unions, heavily rely on legacy systems that may require significant planning and investment to upgrade. However, recognizing the need to remain competitive and meet evolving customer expectations, many banks are now prioritizing the modernization of their systems.
Figure 2 in the report illustrates the contrast between legacy and digital DNA attributes in the financial services industry. Legacy cultural attributes, such as resistance to change, siloed work style, hierarchical organizational structure, and a cautious risk appetite influenced by regulations, act as barriers to digital transformation. On the contrary, digital DNA behaviors, like agility, collaboration, distributed organizational structure, a bold risk appetite, and a customer-centric approach, foster an environment that empowers companies to thrive in the digital landscape.
Recognizing the challenges and limitations imposed by legacy systems, financial institutions are now reevaluating their strategies and seeking ways to modernize their systems. The potential benefits of modernization are significant.
4 Key Reasons for Legacy System Modernization
Embarking on a legacy software modernization project may seem unnecessary to some businesses. If it isn't broken, why fix it? To answer this, you must consider the latent dangers in legacy systems - their vulnerability, incompatibility with new products, or lack of modern functionality. These issues could lead to security threats, an inability to remain competitive, and an inability to retain or attract customers.
Your company's operational software might be functional, but it can obstruct innovation and competitive edge.
Balancing the maintenance of legacy systems with readiness to scale as per customer requirements can be challenging. If you need additional persuasion to modernize your legacy system, below are the top reasons.
High Maintenance Costs
Around five years post-product release, legacy system upkeep costs may surpass the original development budget. This primarily involves managing old codes and responding to support tickets, which could take days to resolve.
Instead of launching new services, you might find yourself persistently addressing urgent issues. Furthermore, as time passes, the number of specialists qualified to work with obsolete technologies will drastically reduce, making their services hard to find and costly.
Limited Support and Lack of Skills in the Market
Business owners may encounter circumstances where their legacy system is no longer supported by the vendor. This also implies that the system is no longer maintained for compliance with current security standards.
For custom-developed systems, there may come a time when finding skilled personnel adept with obsolete technologies for maintenance becomes nearly impossible. Young developers tend to focus on mastering new languages for their CVs, avoiding dealing with legacy code. On the other hand, supporting updated applications is simpler and doesn't require expensive training for dedicated staff.
Inability to Incorporate New Features
The incorporation of new features is fundamental to business growth and success. It assists in staying competitive and meeting customer expectations. Often, new features necessitate integration with a third-party tool or service, and if the business relies on an incompatible legacy system, this may not work or function as expected.
When implementing new features becomes impossible, or the legacy software becomes incompatible with contemporary systems, it signals the need for an upgrade. This will foster interaction with other systems, significantly enhancing system performance and efficacy.
Inadequate Security
One of the major arguments for legacy system modernization is to attain robust security. What was considered secure when the system was created may now pose a risk. Outdated systems fail to match modern ones regarding vulnerability to cyberattacks or data breaches. Compliance with process regulation standards is also a critical factor. Noncompliance with software compliance norms like HIPAA, PCI, SOX, etc., can incur millions in costs.
All aforementioned reasons are strong cases for moving to a well-supported technology with development tools. The legacy system modernization will enable your business to get the most value out of developing new products and launching new features.
Examples of Legacy Systems In Finance
As the financial industry has evolved, various legacy systems have remained constant, often hindering institutions' ability to innovate and grow. These systems, although once at the forefront of technology, have become outdated, and unable to keep up with the demands of the modern age. Here are some prime examples of legacy systems prevalent in the financial industry:
COBOL-Based Systems
COBOL or "Common Business-Oriented Language" represents one of the earliest programming languages. Despite its age, COBOL remains a mainstay in the financial industry, with many large institutions relying heavily on COBOL-based legacy systems. These systems often come with increased operational expenses due to their maintenance and limited scalability. The complex infrastructure makes it challenging to integrate newer systems, limiting collaboration and stifling modernization.
Manual Ledgers and Paper-Based Documentation
Many traditional financial institutions still rely on manual ledgers and paper-based documentation to record transactions. While these methods may seem quaint, they can result in an excessive amount of manual labor, making record-keeping both time-consuming and error-prone. The immediate drawback of these legacy systems includes cumbersome data entry, the inability to collate information digitally, and reliance on physical storage that easily exposes sensitive client information to theft or damage.
Excel Sheet-Powered Systems
Excel sheets are limited in capabilities when subjected to dealing with complex financial instruments, transactions, and regulatory requirements – a pitfall of legacy systems that rely heavily on Excel. The range of automated features needed for modeling and analysis of transactions may not integrate efficiently with the larger financial system, leading to a cumbersome process, errors in calculation, and reporting inefficiency.
Legacy Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Some financial institutions have outdated CRM systems that can't handle the demands the modern customer interface presents. The systems may not integrate with the latest social media or transaction recording technology or track customer preferences accurately. As a result, the bank struggles to provide personalized customer interactions that lead to customer engagement and growth.
In conclusion, the reliance on these antiquated systems presents significant challenges to the financial industry, in part due to the inability to innovate and compete effectively with institutions that have digitally transformed. While these legacy systems are reminiscent of simpler times in the past, the future of finance demands institutions move forward with technologies that allow for exponential growth and efficiency.
Legacy System Modernization Strategies: Three-Step Evaluation Process
Legacy system modernization is a complex task requiring careful planning and strategic decision-making. To maximize effectiveness and ensure the most suitable approach, it is recommended to follow a three-step evaluation process.
STEP 1: Assess legacy systems using six key factors
Six primary factors drive application modernization, such as challenges or limitations created by the legacy application's technology, architecture, or functionality.
Three of these factors stem from a business perspective – business fit, business value, and agility. If the legacy application fails to meet new digital business requirements, it must be modernized to align properly and upgraded to offer increased business value. Applications that lack the agility to adapt to digital business demands might pose cost or risk liabilities.
The other three factors originate from the IT perspective – cost, complexity, and risk. If the total cost of ownership is too high, the technology is overly complex, or security, compliance, support, or scalability gets compromised, modernization is necessary.
The best modernization opportunities are those with numerous factors from both the business and IT perspectives.
STEP 2: Examine modernization options
Once you pinpoint the opportunity and identify the problem, examine the modernization alternatives. Gartner has ranked seven alternatives based on their ease of implementation (the easier, the lesser risk and impact on the system and business processes; the harder, the greater risk and impact).
- Encapsulate: Extend application features by encapsulating its data and functions and making them available as services through an API.
- Rehost: Move the application component to another infrastructure (physical, virtual, or cloud) without changing its code, features, or functions.
- Replatform: Migrate to a new runtime platform with minimal code changes, but without altering the code structure, features, or functions.
- Refactor: Restructure and optimize existing code (while preserving its external behavior) to eliminate technical debt and enhance nonfunctional attributes.
- Rearchitect: Significantly modify the code to adapt it to a new application architecture, leveraging new and improved capabilities.
- Rebuild: Redesign or rewrite the application component from scratch while preserving its scope and specifications.
- Replace: Completely eliminate the previous application component and substitute it, taking into account new requirements and needs simultaneously.
STEP 3: Select the modernization approach with the highest impact and value
Lastly, choose the modernization approach that provides the most significant impact and value to your organization by mapping the seven options in terms of their influence on technology, architecture, functionality, cost, and risk.
In essence, modernizing legacy applications involves deciding between rearchitecting, rebuilding, or replacing. While rearchitecting presents medium costs and risks, rebuilding or replacing results in better outcomes at higher costs and risks. The key is to evaluate all the alternatives to help identify which will achieve the desired result with minimal effort and maximum positive impact.
Legacy System Modernization Approaches
As the financial industry grapples with the challenges posed by legacy systems, updating legacy systems through fintech collaboration emerges as a promising solution. Collaboration with FinTech companies offers a pathway towards modernization, enabling financial institutions to unlock a new world of possibilities. Below are some of the advantages that collaboration can offer.
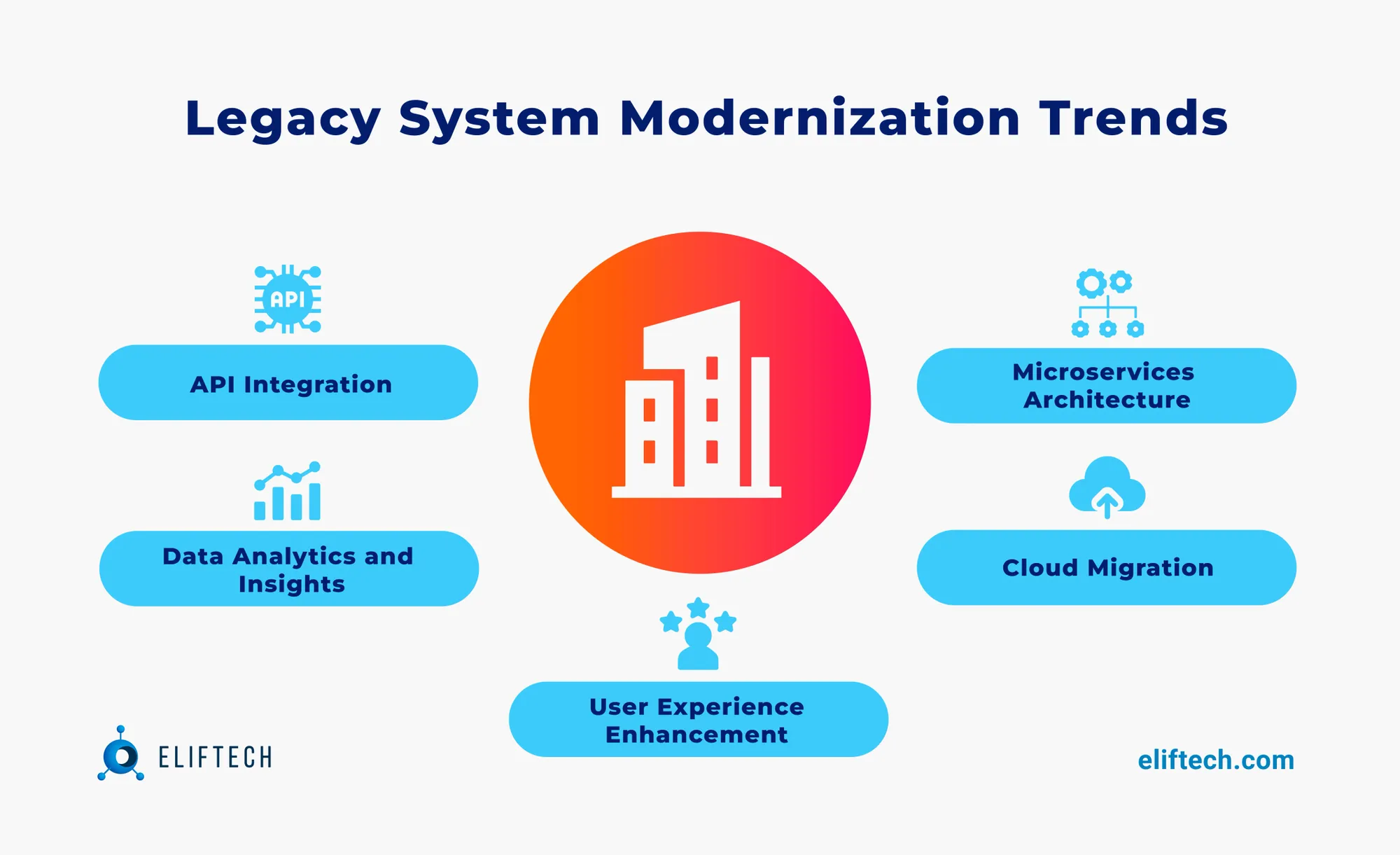
API Integration
Financial institutions can surpass the limitations imposed by legacy systems with the assistance of FinTech companies. Providing API integration, fintechs can help institutions bridge the gap between their outdated systems and modern-day technology. This integration promotes interoperability between systems, allowing for seamless data exchange. It enables the creation of innovative products that serve clients better, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Access to Data Analytics and Insights
The rise of big data analytics has transformed the financial landscape, allowing institutions to harness vast amounts of valuable customer data and gain insights into their operations. In collaborating with FinTechs, institutions can access cutting-edge data analytics technologies, enabling them to develop new offerings and improve existing processes. Utilizing these insights, institutions can customize their services to cater to the ever-changing requirements of their clients.
Microservices Architecture
The monolithic architecture of legacy systems presents a major challenge. Using microservices for legacy software modernization enables institutions to break these systems down into smaller, modular components that are easier to develop, deploy, and maintain. Through collaboration with FinTech companies, institutions can leverage this architecture to modernize their legacy systems. This results in a more efficient and scalable IT infrastructure, promoting agility and innovation.
Cloud Migration
Deciding on enterprise cloud software for legacy modernization organizations can reduce infrastructure costs, enhance security, and improve adaptability. Cloud migration can also increase accessibility and mobility for end-users, making their experience more seamless and enjoyable. By partnering with FinTech companies, institutions can leverage the expertise required to migrate their systems to the cloud, facilitating faster and more efficient adoption.
User Experience Enhancement
Legacy systems often lack the user-friendly interfaces modern customers have come to expect. By collaborating with FinTech companies, institutions can develop user-centered interfaces with engaging designs, intuitive navigation, and seamless functionality. These enhancements lead to an improved user experience and can drive increased customer engagement and loyalty.
In conclusion, the collaboration between financial institutions and FinTech companies presents a significant opportunity for modernization in the financial industry. Leveraging the latest technologies and innovations, institutions can break through the limitations of legacy systems and meet the ever-increasing needs of the modern-day world.
Modernize Your Legacy System with ElifTech
In the ever-evolving financial industry, legacy systems can impede growth and hinder innovation. To overcome these challenges, financial institutions are increasingly turning towards collaboration with FinTech companies. Embracing this collaborative approach yields a multitude of benefits in the modernization of legacy systems and the acceleration of digital transformation. Here's an overview of the key advantages of legacy system modernization services:
- API Integration: FinTech collaboration enables seamless integration between legacy systems and modern technology, promoting data exchange and innovation.
- Data Analytics and Insights: Partnering with FinTechs grants access to advanced data analytics tools, empowering institutions to make informed decisions and provide personalized offerings.
- Microservices Architecture: Breaking down monolithic legacy systems into modular components fosters agility, scalability, and innovation in development, deployment, and maintenance.
- Cloud Migration: Migrating legacy systems to the cloud reduces costs, improves security, and enhances accessibility, benefiting institutions and their customers.
- User Experience Enhancement: Collaboration with FinTechs enables institutions to develop user-friendly interfaces, enhancing customer experience and engagement.
To embark on this transformative journey, businesses can consider partnering with reputable and experienced legacy system modernization companies like ElifTech. As a leading FinTech software development company, we offer legacy software modernization services and expertise in building industry-leading applications for the finance industry.
Ready to modernize your legacy system? ElifTech as a legacy software modernization company can help to drive your institution's digital transformation. Let us know about your project in mind.
Browse our case studies and get actionable insights to drive your success
See more