Logistics
What Features of EDI vs API Logistics Can Use For Improved Performance
Every second and data point counts when it comes to B2B communication and data exchange throughout the logistics ecosystem. Well-established EDI and modern API logistics technologies make this communication and managed data transfer seamless and reliable.
Some organizations may find them similar to some extent, and others may think of APIs as a modern technology that came to replace EDI. However, even if they have the same function, they still have differences in terms of what capabilities they have and what they are best suited for.
In this blog post, we'll focus on both data exchange technologies, talk about what they're good at, what they're limited to, and give you clear insights to pick the right one for your business.
Mastering data interchange in logistics? EDI and API are your strategic assets
Data interchange in logistics means exchanging data among multiple entities involved in a single supply chain or industry. Data interchange in logistics allows companies to share information about their inventory, production levels and other pertinent details. This allows companies to coordinate their efforts better, as well as improve efficiency through greater visibility into each company's operations. There's small wonder people with solid professional background keep googling things like "API logistics meaning", sincfe logistics API and EDI are at the forefront, establishing themselves as pivotal players in data exchange.
How does EDI work in logistics?
EDI works by first connecting to a secure P2P network. It takes paper documents, turns them into digital data, and helps replace traditional tasks like mailing invoices and shipping notices with a modern digital process. It translates data into a mutually agreed standardized format for fluid communication between trading partners. These standardized EDI files are converted into proprietary formats that sync with backend systems smoothly. The process is bidirectional, capable of initiating from an ERP system or directly from a trading partner, ensuring flexible and efficient data interchange in line with your business objectives.
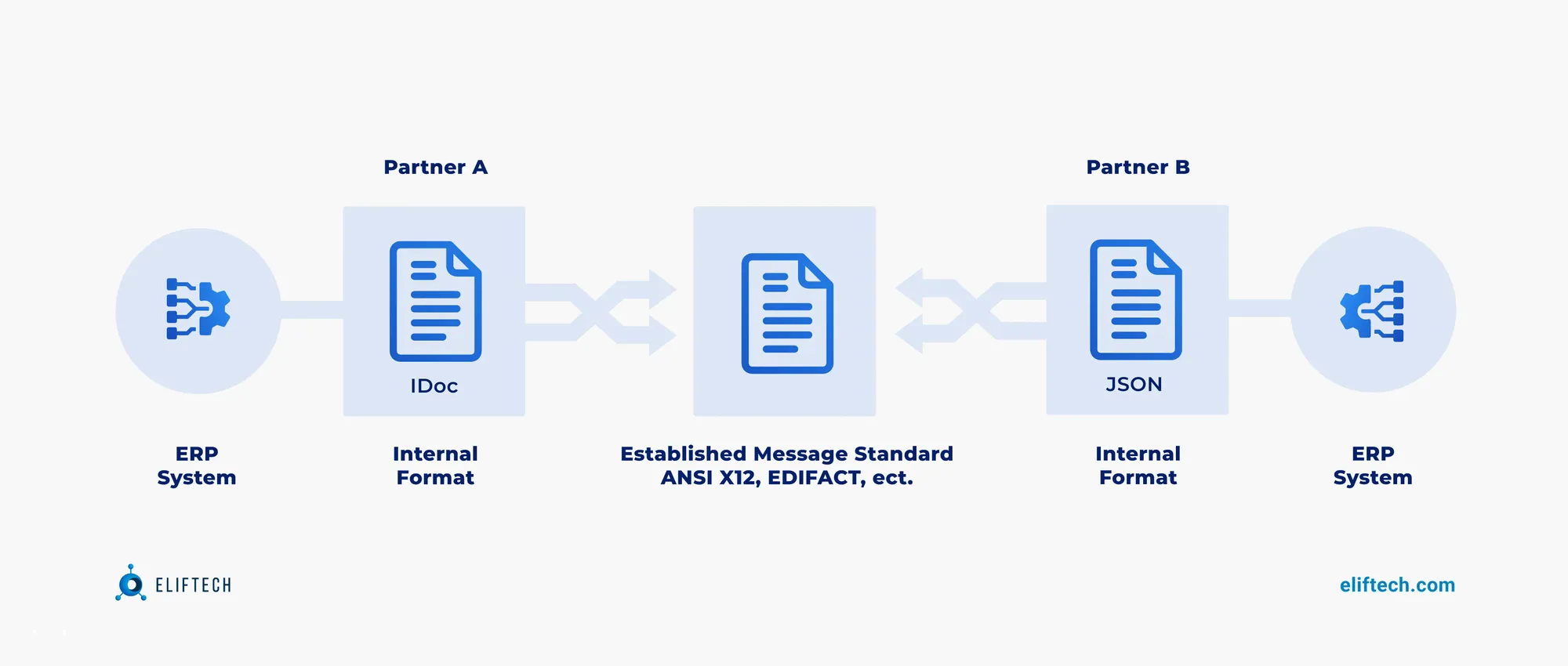
EDI protocols have been woven intrinsically into the fabric of logistics processes, driving improvements in areas such as procurement, inventory management, transportation, and invoice processing. Such broad applications have led to its universal adoption, with over 85% of global electronic business transactions currently conducted via EDI, according to a comprehensive report by Deloitte.
EDI serves multiple logistic demands:
- Order management – This includes order entry, fulfillment, pricing and inventory management.
- Shipping – This includes pickup/delivery confirmation, load consolidation and tracking reports.
- Shipping documents – This includes bills of lading, airway bills and invoices.
- Warehouse Management – EDI aids in tracking inventory within warehouses, enhancing efficiency.
- Product Information – EDI provides a platform for exchanging accurate product and packaging details, improving communication and customer satisfaction.
- Financial transactions – EDI streamlines financial processes like invoicing and electronic funds transfer, encouraging swift and secure transactions.
What is API in logistics? Are these enhanced EDI?
While EDI and APIs perform the same function: transferring data, EDI is a network-based tool that makes this transfer possible between two EDI systems, while APIs rely on cloud technology to enable data transfer in less than a second between more systems. This flexibility becomes a major ground for businesses to choose API over EDI.
Unlike EDI, APIs transmit data in real-time; they don’t rely on a specific format; real-time data transmissions are fully automated, and they are way easier and less expensive to set up and maintain than EDI. This flexibility positions APIs as an attractive alternative to EDI due to attributes such as:
- Real-time data transmission.
- Automation of data transmissions.
- Diverse format compatibility.
- Simplified set-up and maintenance.
EDI vs. API: Is this a choice to make?
It is important to note here that APIs logistics are now widely considered as a new, more sophisticated data exchange technology. Despite this, EDI remains the dominant and reliable industry standard that solves the most critical business needs.
However, the choice between API and EDI is not a simple one. A survey of 200 supply chain executives demonstrates this complexity, with less than 25% viewing EDI as the lone future of B2B communication. It suggests an evolving B2B landscape, where EDI becomes part of a broader strategy, possibly augmented by APIs.
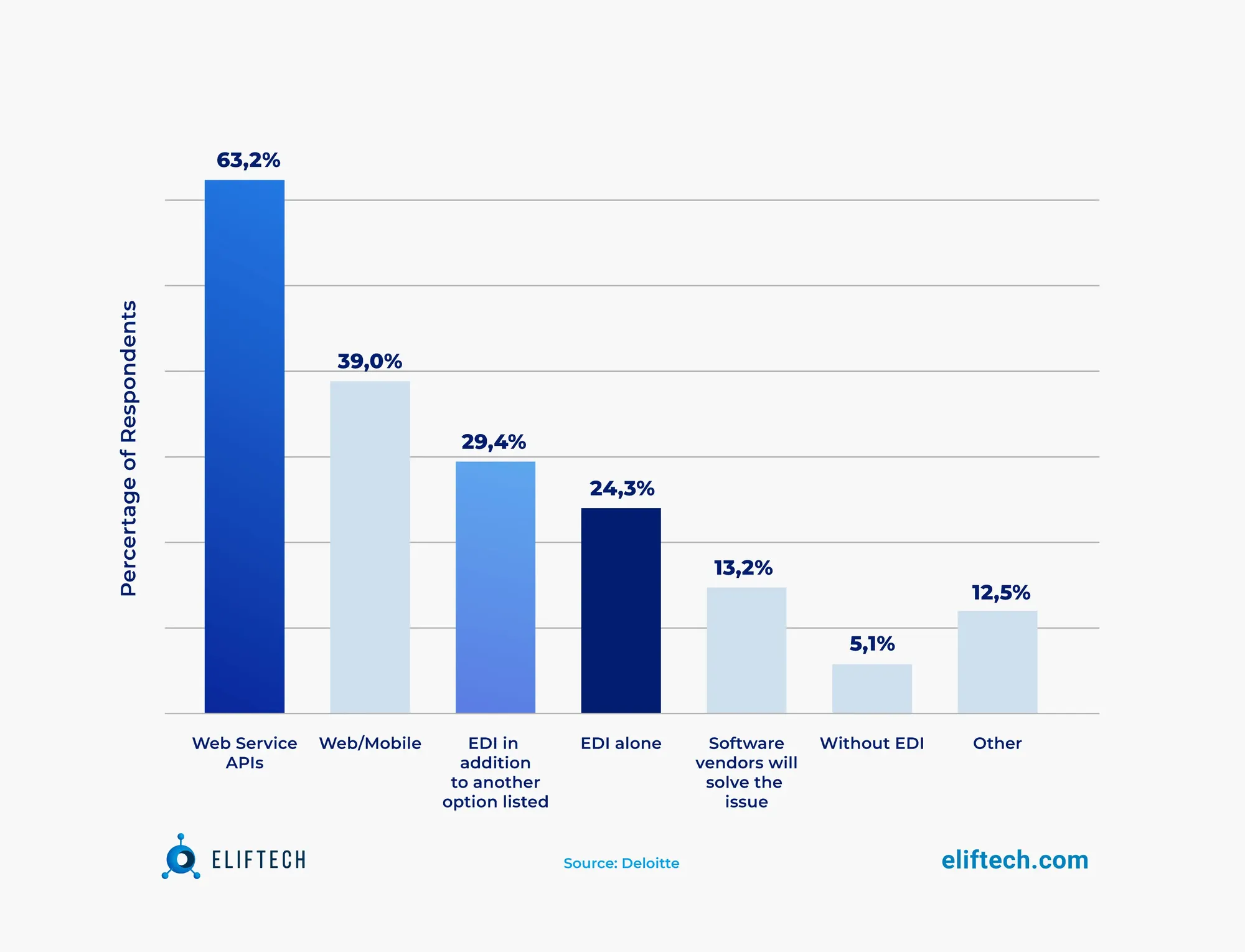
Moreover, APIs are making a substantial mark, enhancing real-time updates and enhancing supply-chain visibility. They foster an environment conducive to prompt decision-making and problem-solving. By 2023, it is projected that over 50% of B2B transactions will be conducted through real-time APIs as against traditional models.
These insights lead us to a crucial inflection point: Given the pivotal role data interchange plays in logistics, the question becomes not whether to adopt EDI or API, but how best to leverage these technologies to fuel your business growth?
The distinctions between EDI and API
While APIs present numerous benefits, the EDI vs. API decision isn't uniform across businesses. EDI's established presence in modern logistics often makes enterprises hesitant to shift to new solutions. Ultimately, the right choice aligns with your broader business strategy and growth objectives.
At this point, a defining question emerges: what are the key differences between EDI and APIs, and how do these dissimilarities impact their practical applications in logistics?
The following table shows the characteristics of EDI and APIs, spotlighting their unique features:
API and EDI in logistics as of 2023
EDI continues to be a reliable backbone, ensuring standardized and structured data transmission, particularly ideal for batch processing of mission-critical transactions like financial documents. The logistics industry heavily relies on EDI for various functions related to commerce and supply chains, such as order processing, invoicing, and procure-to-pay. The increasing adoption of EDI is projected to drive the global EDI market size to USD 4.52 Billion by 2030.
And, yes, EDI might seem outdated in some respects. However, it has long been a globally established standard in the logistics industry, especially among industry giants. Many of these players find no viable alternative that surpasses EDI in a way that justifies replacing existing EDI connections with their major partners.
APIs “come on the heels,” offering real-time data exchange capabilities and instant connectivity, which are exceptionally vital for the uncertain future we are heading towards. They excel when there's a need to connect directly to transactional systems or enable real-time data exchange. In contrast, EDI lacks the capacity for real-time information exchange as it relies on asynchronous batch data exchange.
So, while EDI is well-established, proven, and cost-effective, the adoption of logitics API integration is rapidly growing for two primary reasons:
- APIs are making traditional EDI even better by enabling real-time data exchange, including important details like location data and trucking spot rates.
- There is a noticeable trend of APIs replacing EDI, particularly as 3PLs, digital freight brokerages (DFBs), and technology-enabled TMS and WMS incorporate APIs into their platforms.
This shift has resulted in a much faster adoption of APIs in supply chain management compared to EDI, and this trend is expected to continue accelerating.
However, this doesn't mean that these two technologies will compete for the title of the best data exchange method in the near future. In fact, it may go against our expectations. To keep the supply chain moving forward, pivoting isn't a practical choice. It's evident that the best decision would be to enhance the capabilities of EDI integration with API logistics to address the limitations of both technologies.
When to use EDI for structured, batch-oriented data exchange in long-term standardized B2B transactions? Or when would API be more appropriate for scenarios requiring real-time data and integration with various systems? Contact ElifTech specialists today for consultation.
When to сhoose EDI vs. API for your logistics projects
Choosing between EDI and APIs depends on the specific needs of your logistics projects. A successful data integration strategy involves understanding your technology landscape and balancing the needs of customers, partners, suppliers, internal teams, and your future enterprise plans.
EDIs are for structured, batch-oriented data exchange in long-term standardized B2B transactions. Recent updates can potentially integrate seamlessly into a modern and future-ready supply chain.
Use EDIs for
- Order Processing - EDIs are ideal for structured, batch-oriented data exchange in processes like order placement and processing.
- Shipment Tracking - when you need to track shipments in a standardized manner.
- Inventory Management - especially for managing inventory levels and updates efficiently.
- Shipping Documentation - EDIs excel in managing shipping-related documents and data.
- Customs and Compliance - EDIs are a solid choice for ensuring compliance with customs regulations.
Consider EDIs when:
- Dealing with Legacy Systems - EDIs work well with older, well-established systems.
- Handling High Data Volume - for large-scale data exchange.
- Engaging in B2B Transactions - where standardized and structured data exchange is critical.
- Seeking Long-Term Partnerships - work well in scenarios involving enduring partnerships, as they are well-suited for consistent, standardized data transfer over time.
APIs are for scenarios requiring real-time data and integration with various systems, making them ideal for modern e-commerce and logistics operations. The data-driven nature of APIs is a crucial element that cannot be ignored as businesses increasingly become interconnected. APIs have the capability to establish connections among various organizational units both within and outside your company.
Use APIs for
- Real-Time Logistics Tracking API - APIs are excellent for tracking and monitoring in real-time
- Dynamic Pricing - when you must adjust pricing dynamically based on various factors.
- Inventory Sync - especially for keeping inventory data up to date across systems.
- Order Fulfillment - APIs offer agility in managing order fulfillment processes.
- Third-Party Integrations - when you need to integrate with various third-party systems seamlessly.
Consider APIs when:
- Dealing with Real-Time Interactions - for scenarios requiring immediate data exchange.
- Working in the E-commerce niche - APIs are essential for the fast-paced world of online commerce.
- Ambitious about Scalability - when your logistics operations are growing and need to scale.
- Need Data Enrichment - APIs can enrich data with real-time information.
Can the Two Coexist?
We don’t think of APIs as a panacea for B2B. Even though Gartner projected that 50% of transactions would be through APIs by the end of 2023, this only confirms that EDI will still support 50% of all remaining transactions.
Application leaders responsible for upgrading integration strategies and infrastructure should keep this in mind as there’s a more interesting solution for them - they can upgrade their B2B integration strategy by simply integrating API capabilities into existing EDI setup, avoiding the need for a separate infrastructure or doubling-up investments in APIs.
With no clear winner, a hybrid EDI/API solution is a more reasonable option. It combines EDI's strengths with the accessibility of APIs, simplifying some EDI complexities through a modern API integration logistics need.
Notable Case Studies
Caraway, a company that sells home goods, streamlines operations, and reduces expenses through EDI modernization
Business Challenge:
Caraway's previous EDI infrastructure had slow onboarding timelines, a lack of responsiveness, and outdated user experience. Caraway needed to speed up onboarding, simplify EDI processes for their staff, and improve customer support.
Solution:
Caraway chose to modernize EDI-managed services.
Results:
- Streamlined onboarding from 12 weeks to two weeks.
- Achieved up to 30% reduction in EDI costs.
- Managed EDI relationships with only one employee.
- Increased operational agility.
Sethmar Transportation, a third-party logistics (3PL) provider, modernizes its EDI infrastructure to improve onboarding processes and maintain competitive service levels.
Business Challenge:
Sethmar Transportation had limited visibility and control over their shipments due to their existing EDI solution. This lack of robustness made it challenging for them to onboard new customers and optimize their processes efficiently. They needed a solution that would offer greater control, visibility, and scalability.
Solution:
Sethmar adopted a modern EDI platform that served as a central system to manage their EDI operations. With this platform, they gained better control over onboarding new partners, managing all EDI relationships in the cloud, integrating with their existing TMS platform, and ensuring uninterrupted business transactions.
Features Delivered:
- Accelerated onboarding and the ability to work with new customers efficiently
- Reduced time spent on EDI troubleshooting and costs
- Improved automation, reducing manual data entry errors and enhancing overall efficiency.
Results:
- Configured EDI connections in less than 48 hours
- Reduced time spent on EDI troubleshooting each month through process optimization
- Onboarded 17 trading partners with no EDI expert on staff
MercuryGate, a leading TMS provider, implements (less-than-truckload) LTL APIs to enhance workflows and improve efficiency in freight transportation
Features Implemented:
- Ability to receive LTL quotes for volume, contract, broker pricing, and transit schedules from multiple carriers
- Self-assigning PRO numbers prior to pick-up
- Use of Electronic Bills of Lading (eBOL) to digitally transmit shipping information to carriers quickly and securely
- Digital pickup scheduling and immediate pickup confirmation
- Real-time shipment monitoring and messaging
- Access to vital documents (including bills of lading, weight & inspection certification, proof of delivery, and invoices)
- Proactive supply chain management with real-time alerts.
Value Delivered:
- Streamlined workflows, automation of manual processes
- Improved efficiency and resource utilization
- Enhanced data exchange with customers
Results:
- Cost reduction
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Faster implementation and data exchange capabilities (Compared to traditional EDI setups, the implementation of LTL APIs had a significantly shorter setup time, enabling faster deployment and data exchange with customers.)
Conclusion
No matter your B2B integration approach, the choice between EDI and API is not a matter of one being superior to the other but rather a strategic blend of their strengths. So, when faced with the EDI vs. API dilemma, remember that the power is in their combination, providing the best of both worlds for a seamless, efficient, and forward-looking logistics ecosystem.
Contact ElifTech specialists for guidance in building a strong architecture that effectively combines the strengths of EDI’s tried-and-true resilience, flexibility, and maturity with the modern speed and agility of APIs where needed.
Browse our case studies and get actionable insights to drive your success
See more